About
16 March 2021
New Imaging Technology Could Help Predict Heart Attacks
Preclinical testing shows intravascular imaging approach can detect unstable coronary plaque
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a new intravascular imaging technique that could one day be used to detect coronary plaques that are likely to lead to a heart attack. Heart attacks are often triggered when an unstable plaque ruptures and then blocks a major artery that carries blood and oxygen to the heart.
“If unstable coronary plaques could be detected before they rupture, pharmacological or other treatments could be initiated early to prevent heart attacks and save lives,” said research team leader Seemantini Nadkarni from the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital. “Our new imaging technique represents a major step toward achieving this.”
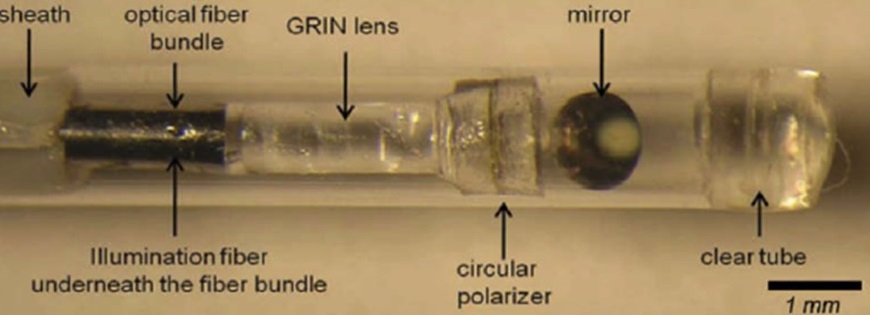
Caption: A new technique known as intravascular laser speckle imaging could one day be used to detect coronary plaques that are likely to lead to a heart attack. The researchers developed a small diameter intravascular catheter that incorporates a small-diameter fiber bundle, polarizer and GRIN lens to image the reflected speckle patterns onto a CMOS sensor.
Credit: Seemantini Nadkarni, Wellman Center for Photomedicine
In The Optical Society (OSA) journal Biomedical Optics Express, the researchers report a preclinical demonstration of their new intravascular laser speckle imaging (ILSI) technique in a living animal model. They show, for the first time, that ILSI can identify the distinct mechanical features of plaques that are most likely to rupture under physiological conditions of cardiac motion, blood flow and breathing.
“Reducing mortality from heart attacks in the general population requires a comprehensive screening strategy to identify at-risk patients and detect high-risk vulnerable plaques while they can be treated,” said Nadkarni. “By providing the unique capability to measure mechanical stability — a critical metric in detecting unstable plaques — ILSI is poised to provide a new approach for coronary assessment.”
Capturing mechanical stability of plaques
Although intravascular technologies have been developed to evaluate microstructural features of unstable plaques, recent studies have shown that mechanical features, in addition to microstructural and compositional features, influence plaque rupture.
“Measurement of the plaque mechanical properties is crucial in identifying unstable plaques with a propensity for rupture and subsequent heart attack,” said Nadkarni. “ILSI provides the unique capability to quantify an index of mechanical properties of coronary plaques, thus providing a direct assessment of mechanical stability.”
To estimate mechanical properties, ILSI uses laser speckle patterns that are formed when laser light is scattered from tissue. When viewed with a high-speed camera, the speckles fluctuate in time due to the viscoelastic properties of the plaque. This allows the researchers to measure and discriminate the mechanical properties of unstable plaques, which tend to be rich in lipids.
“For this new study, we developed a small diameter intravascular catheter that incorporates an optical fiber that delivers light to the coronary artery wall,” said Nadkarni. “We also used a small-diameter fiber bundle, polarizer and GRIN lens to image the reflected speckle patterns onto a CMOS sensor.”
For preclinical testing, the researchers evaluated the ability of their ILSI instrument to detect unstable plaques in a human coronary to swine xenograft model. This model system uses human coronary arteries that are sutured onto the beating heart of an anesthetized living pig. They assessed the mechanical properties of plaque inside the arteries by calculating the rate, or time constant, of fluctuations in the intensity of the speckle pattern and then compared their results with histopathological findings.

Caption: The researchers showed that ILSI can be used to identify plaques that were most likely to rupture under physiological conditions. Pictured is the animal catheterization laboratory with the portable ILSI system on the cart (right).
Credit: Seemantini Nadkarni, Wellman Center for Photomedicine
“The time constants in unstable plaques were significantly and distinctly lower than other stable plaques in the coronary wall,” said Nadkarni. “These results demonstrated the exquisite diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of ILSI for detecting human lipid pool plaques that were most likely to rupture under physiological conditions.”
The researchers say that the new technique could be easily integrated with other intracoronary technologies such as optical coherence tomography or intravascular ultrasound to combine the mechanical findings from ILSI with morphological information to improve the evaluation of plaque stability.
The researchers plan to continue to evaluate the capability of their ILSI instrument for rapid assessment of the coronary vasculature in live animals. Once these preclinical studies are complete, they will assess the safety of the catheter for use in humans and then begin the process of gaining regulatory approval for clinical use.
Paper: Z. Hajjarian, J. D. Toussaint, J. L. Guerrero, S. K. Nadkarni, “In-vivo mechanical characterization of coronary atherosclerotic plaques in living swine using intravascular laser speckle imaging,” Biomed. Opt. Express, volume 12, issue 4, pp. 2064-2078 (2021).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1364/BOE.418939
About Optica Publishing Group
Optica Publishing Group is a division of the society, Optica, Advancing Optics and Photonics Worldwide. It publishes the largest collection of peer-reviewed and most-cited content in optics and photonics, including 18 prestigious journals, the society’s flagship member magazine, and papers and videos from more than 835 conferences. With over 400,000 journal articles, conference papers and videos to search, discover and access, our publications portfolio represents the full range of research in the field from around the globe.
About Biomedical Optics Express
Biomedical Optics Express serves the biomedical optics community with rapid, open-access, peer-reviewed papers related to optics, photonics and imaging in biomedicine. The journal scope encompasses fundamental research, technology development, biomedical studies and clinical applications. It is published monthly by Optica Publishing Group and edited by Christoph Hitzenberger, Medical University of Vienna, Austria. For more information, visit Biomedical Optics Express.
About The Optical Society
The Optical Society (OSA) is dedicated to promoting the generation, application, archiving, and dissemination of knowledge in optics and photonics worldwide. Founded in 1916, it is the leading organization for scientists, engineers, business professionals, students, and others interested in the science of light. OSA’s renowned publications, meetings, online resources, and in-person activities fuel discoveries, shape real-life applications and accelerate scientific, technical, and educational achievement.
About Biomedical Optics Express
Biomedical Optics Express serves the biomedical optics community with rapid, open-access, peer-reviewed papers related to optics, photonics and imaging in biomedicine. The journal scope encompasses fundamental research, technology development, biomedical studies and clinical applications. It is published monthly by Optica Publishing Group and edited by Christoph Hitzenberger, Medical University of Vienna, Austria. For more information, visit Biomedical Optics Express.
Media Contact
